A child domain is a member domain of a Windows 2000 Active Directory directory service
but is not the root domain of that Active Directory. Perhaps the best way to illustrate
the differences between the NT 4.0 domain structure and Windows 2000 is to compare the
old Hokies (NT 4.0) domain to the new Hokies (W2k) domain.
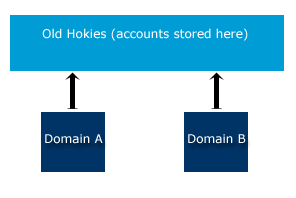
Old Hokies was an NT 4.0 accounts domain with which other NT 4.0 domains established a
one-way trust to allow users with a Hokies account to access resources in their domain.
With this model, there was no communication between domains unless those domain admins
manually established the trust.
 NT 4.0 Domain Model
NT 4.0 Domain Model
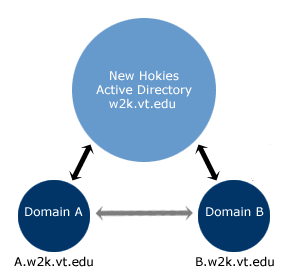
New Hokies is the root domain of Virginia Tech's Windows 2000 Active Directory directory
service; other domains who wish to participate join as child domains. In the Windows 2000
domain model, child domains are more tightly integrated through Active Directory. Child
domains are not as isolated from one another as NT domains were, which is partly the basis
for our
Child Domain Usage Requirements
.
In Windows 2000, two-way, transitive trusts
are automatically established between child domains when they join the tree. This simplifies
sharing resources between domains.
 Windows 2000 Domain Model
Windows 2000 Domain Model