-
Active Directory
-
Two-way, Transitive Trusts
-
Enhanced File Management
-
Terminal Services
Active Directory
Active Directory (AD) is the directory service included with Windows 2000. It stores
information about network objects (computers accounts, user accounts, etc.) and makes
them available to users and administrators from anywhere in the domain tree. Active
Directory provides administrators with a single point of administration for all network
objects.
Some of the benefits of Active Directory include:
-
Enhanced security
For domains in native mode (no NT 4.0 Domain Controllers), Kerberos v5 is the
default authentication protocol. Kerberos enables single sign-on capabilities,
Internet Protocol security (IPSec), and the QoS Admission Control Service.
-
Dynamic DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the primary locator service in Active Directory.
Dynamic DNS removes the need for manual editing and replication of a DNS database.
Dynamic DNS also allows authenticated DHCP servers to update a client's FQDN to IP
address mapping whenever a DHCP lease is issued.
-
Easier domain administration
Active Directory provides the means to organize user and network resources
hierarchically. This can give domain administrators a single point of management
of users, groups, and network resources, as well as the ability to distribute
software and configure user desktops through Group Policy.
Two-way, Transitive Trusts
A trust between two domains allows for access to resources in one domain to be granted
to chosen members of the other domain. For example, if Domain A trusts Domain B, then
the administrator of Domain A can grant access to resources in Domain A to select users
in Domain B.
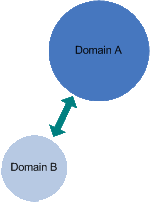 Two-way Trust
Two-way Trust
In Windows 2000, domains that participate in an Active Directory directory service
automatically have two-way, transitive trusts established between them. In the diagram
to the left, Domain A is the root domain of an Active Directory directory service and
Domain B is a child domain.
The trust in this example is two-way because not only does Domain B trust Domain A, but
Domain A trusts Domain B. Therefore, resources in domain A can be granted to users from
Domain B, and visa versa.
The transitive quality of Windows 2000 trusts is demonstrated in the example to the right
when Domain C joins the Active Directory as another child domain. Not only do Domain A and
Domain C have a two-way trust, but Domain B and Domain C have a two-way trust because
they both trust Domain A. This allows Domain B and Domain C to make resources available
to one another without manually establishing the trust.
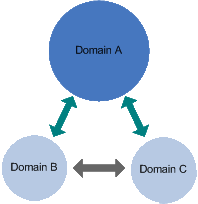 Transitive Trust
Transitive Trust
Enhanced File Management
Compared to NT 4.0, Windows 2000 provides significant enhancements to file management,
including:
-
Disk defragmenting, which NT 4.0 lacks.
-
Disk Quotas: Administrators can set storage limits for users on a volume. Users
are charged for files that they own on a volume. A volume can include different
partitions on the same physical hard disk.
-
Encrypted File System (EFS) uses public key technology to encrypt files or folders.
-
Backup software: Ntbackup is extremely useful for backing up files that the operating
system always has open, such as Active Directory databases and the registry.
-
Distributed File System (DFS) makes it easier for users to locate data on the network.
-
Power Management provides greater overall power efficiency and prolonged battery
life. Especially useful for portable systems.
-
Plug and Play implimentation, similar to Windows 98, makes it easier to install devices.
-
Group Policy allows administrators to manage the desktops of user running Windows
2000 Professional, including which applications they can use.
Terminal Services
Windows 2000's Terminal Services are similar to those of Citrix Winframe/Metaframe. They
allow client machines to access applications running entirely on the server and supports
multiple client sessions. The server manages all computing resources for each client that
is connected to the server and provides each user with her own environment. Terminal Services
are also extremely useful for remote administration of Windows 2000 Server.